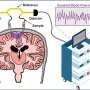
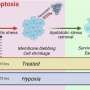
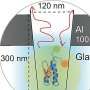
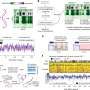
Next-gen interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy achieves 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring
Cerebral blood flow is essential for normal brain function and often perturbed in neurological disease. If one shines a source of coherent light on perfused tissue, the detected speckles, or "grains" of light fluctuate, or "dance," at a rate proportional to blood flow in the