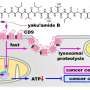
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
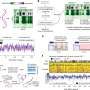
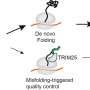
A collaborative research team has uncovered a previously unknown mechanism of action of yaku'amide B, a structurally complex peptidic natural product derived from deep-sea sponge found in the waters near Yakushima Island, Japan. Natural products often exhibit multifaceted