Cell death in photoreceptor cells is reversible, study finds
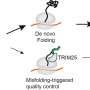
Photoreceptors are specialized cells in the eye that convert light energy into neural signals. Several diseases that cause irreversible vision loss, including age-related macular degeneration, retinitis pigmentosa and retinal detachment, are associated with dying